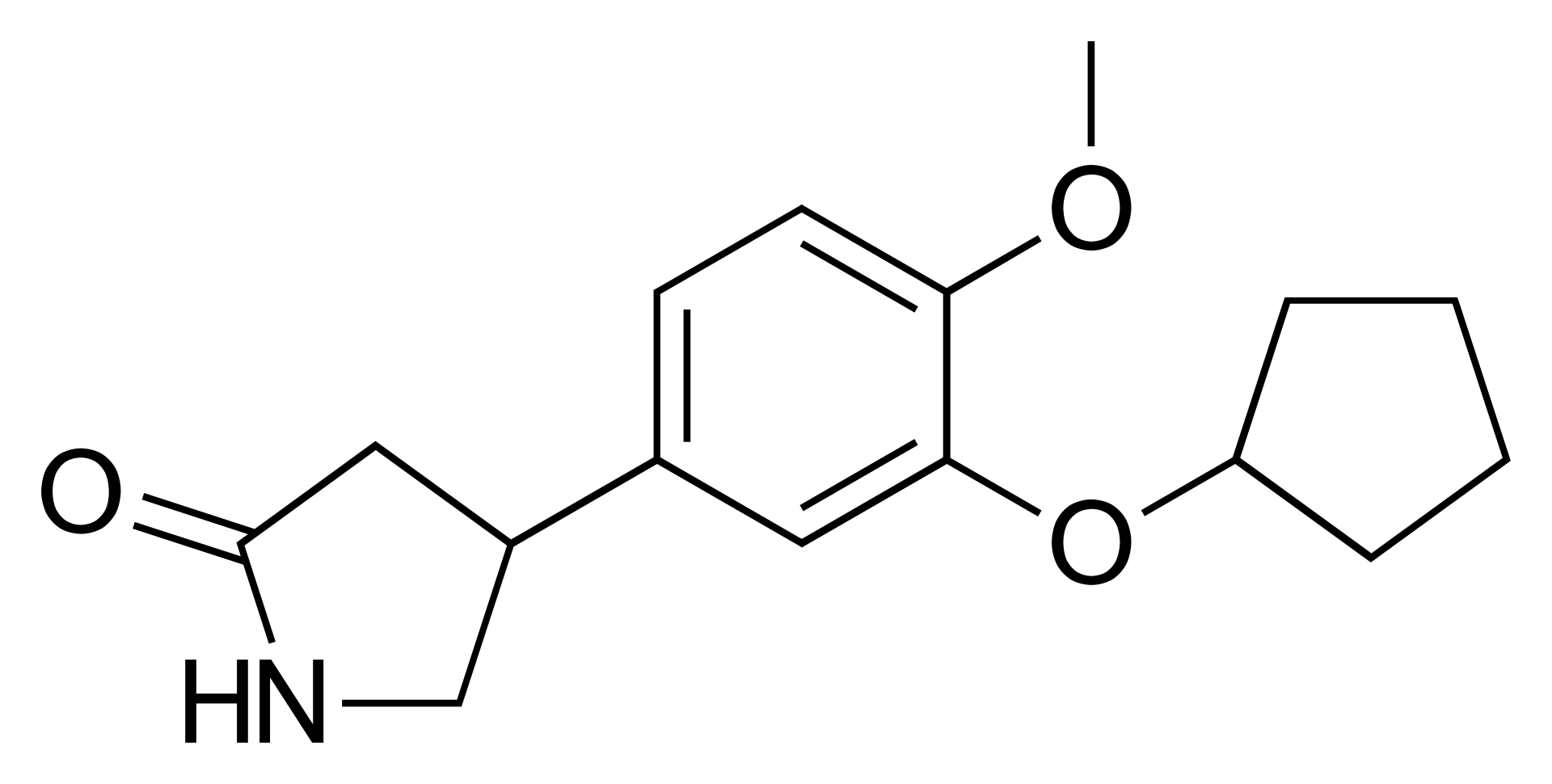
Rolipram
Prototype PDE4 inhibitor (CAS 61413-54-5)
Rolipram is a classical, highly selective PDE4 inhibitor. Though discontinued for clinical use due to GI side effects, it is widely used in research on memory, neurodegeneration, CNS inflammation, and more.
Also known as:
Formula
C₁₆H₂₁NO₃
Category
PDE4 Inhibitor / Cognitive research
Half-life
~3 hours
Bioavailability
~75%
Chemical Profile
Mechanism of Action
Rolipram is a prototype selective PDE4 inhibitor, raising cellular cAMP and modulating neuroinflammation, synaptic plasticity, and protein aggregation pathways. Its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and memory-enhancing activities are prominent in preclinical models, but clinically limited by GI side effects.
Research & Clinical Evidence
Clinical Trials, PK Data in Humans
Oral rolipram is well-absorbed and metabolized in the liver, but clinical development was stopped due to GI side effects and a narrow therapeutic window.
Antidepressant & Neuroprotective Properties
Major preclinical/clinical research demonstrated antidepressant efficacy and cAMP/proteasome-upregulating effects in animal models (Alzheimer’s, etc.), though not tolerated in human dosing.
Broader Research Utility
Continues as a research tool for PDE4/cAMP signaling: used in studies of autoimmune disease, Alzheimer’s, cognitive enhancement, spinal cord injury, and respiratory disorders in animals.
Safety & Side Effects
Narrow window: higher doses cause GI upset (nausea, vomiting); major reason for clinical discontinuation. No significant toxicity at subemetic research doses in animals.
Regulatory & Legal Status
US/EU/International
- Investigational, never marketed or scheduled
- No Rx or OTC status in any region
- Research chemical for academic/industry use only
Note: Research chemical, no human or animal use permitted outside studies.
History
Developed by Schering AG in the early 1990s as a first-in-class PDE4 inhibitor antidepressant. Discontinued after phase trials due to side effects but remains a critical tool compound for neuroinflammation, memory, and CNS signaling research.

Premium Rolipram
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- Prototype and reference PDE4 inhibitor
- Demonstrated effects: neuroprotection, anti-inflammatory, memory
- Standard tool in CNS pharmacology
Considerations
- Abandoned as drug due to GI side effects
- Research only, not for any clinical use
- No human OTC or Rx availability
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References
- Krause, W., et al. "Pharmacokinetics of (+)-rolipram and (−)-rolipram in healthy volunteers." European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, vol. 38, no. 1, 1990, pp. 71–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314807.
- Zhu, J., Mix, E., Winblad, B. "The antidepressant and antiinflammatory effects of rolipram in the central nervous system." CNS Drug Reviews, vol. 7, no. 4, 2001, pp. 387–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1527-3458.2001.tb00206.x.
- McKenna, J.M., Muller, G.W. "Medicinal Chemistry of PDE4 Inhibitors." In: Beavo J, Francis SH, Houslay MD, eds. Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases in Health and Disease. CRC Press, 2006.
- Myeku, N., et al. "Tau-driven 26S proteasome impairment and cognitive dysfunction can be prevented early in disease by activating cAMP-PKA signaling." Nature Medicine, vol. 22, no. 1, 2016, pp. 46–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4011.
- Kumar, N., et al. "Phosphodiesterase 4-targeted treatments for autoimmune diseases." BMC Medicine, vol. 11, 2013, p. 96. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-96.
- "Rolipram." PubChem Compound Summary, NCBI, CID 5092, 2024. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5092
For research and educational reference only. Not for clinical, veterinary, or supplement use. Last updated: 4/12/2025.