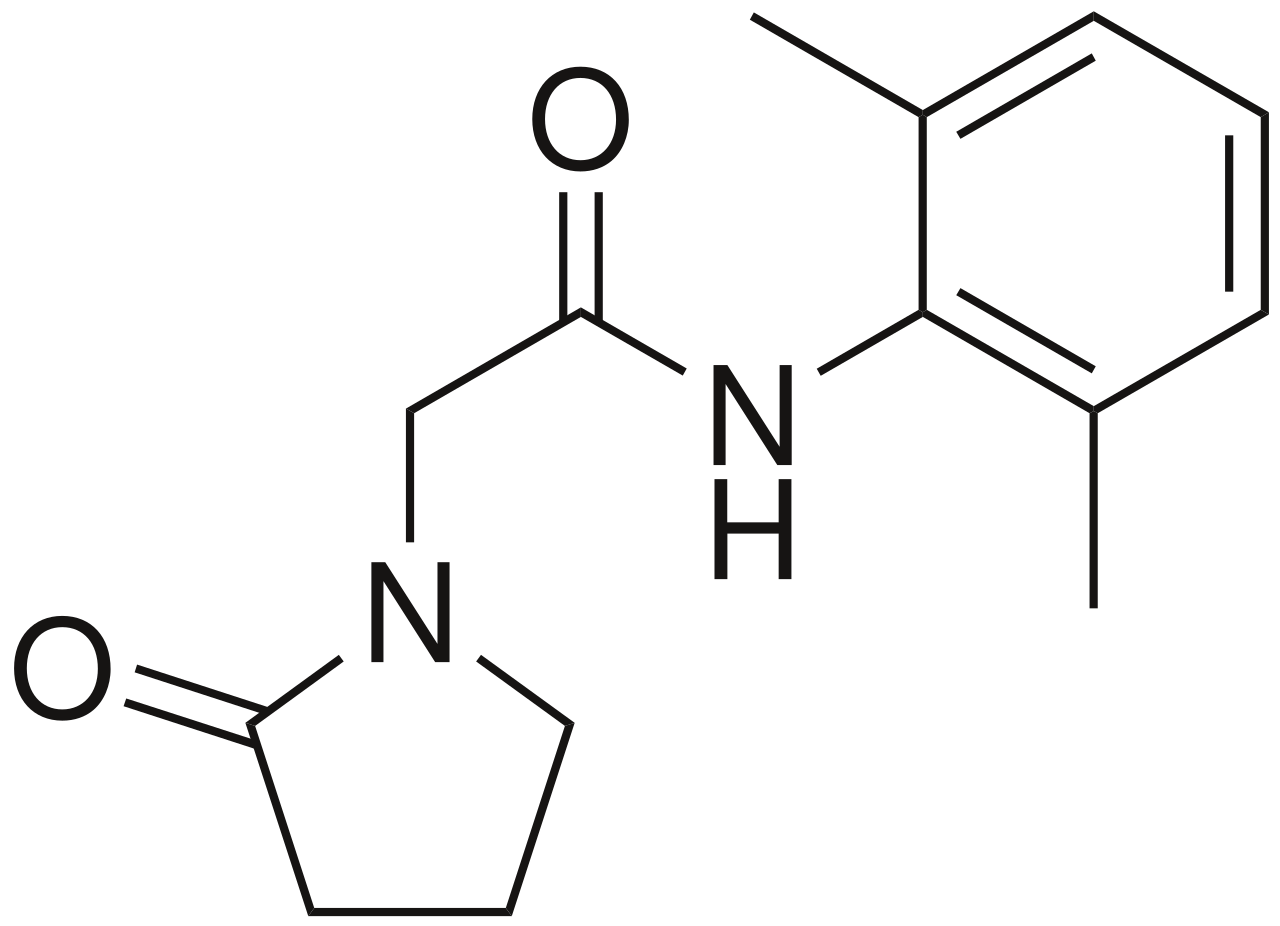
Nefiracetam
CAS 77191-36-7
Nefiracetam is an investigational racetam with experimental clinical and animal evidence for cognitive enhancement, motivation, and neuroprotection, primarily via GABAA receptor modulation. Not FDA/EMA approved; available for research only.
Also known as:
Formula
C₁₄H₁₈N₂O₂
Category
Racetam (GABAergic)
Molar Mass
246.31 g/mol
Legal Status
AU: S4, US/EU: Research only
Chemical Profile
Mechanism of Action
Uniquely among racetams, nefiracetam binds to and modulates GABAA receptors (agonist, IC50~8.5 nM), enhances cholinergic and monoaminergic transmission, and has anti-amnesia and motivational effects in various rodent models.
Preclinical & Clinical Evidence
Pharmacokinetics in Humans
Healthy volunteer studies show rapid oral absorption and short half-life; well tolerated, no toxicity at clinical doses.
Anti-Amnesia & Apathy: Clinical and Animal Data
Animal studies show antiamnesic and nootropic effects across several cognition-impairment models. Small clinical trials showed improved apathy/motivation in post-stroke depression.
GABAA Receptor Modulation, Animal Studies
High-affinity binding and functional effects at GABAA receptors demonstrated in animal models and in vitro, differentiating nefiracetam from classic racetams.
Safety & Side Effects
No toxicity documented in humans/primates at research doses. Renal/testicular toxicity occurs in dogs and (at higher dose) rats via a unique metabolite not produced in humans.
Regulatory & Legal Status
Australia / Global
- Schedule 4 prescription only (Australia)
- Unscheduled, not FDA/EMA approved (US/EU)
- Sold only as research compound globally
Note: Research only. Not approved as medicine or supplement.
History
Synthesized and trialed by Dainippon Sumitomo (1980s–90s), studied for cognitive and post-stroke depression effects. Abandoned for commercial use due to regulatory and market factors.

Premium Nefiracetam
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- Unique GABAA and cholinergic mechanism
- Rodent and preliminary clinical data
- Potential anti-amnesia and motivational effects
Considerations
- No FDA/EMA approval; AU prescription only
- Best evidence: rat and pilot clinical trials
- Not for human use outside research
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References
- Fujimaki, Y., et al. "Single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of nefiracetam in healthy volunteers." J. Pharm. Pharmacol., vol. 44, no. 9, 1992, pp. 750–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb05513.x.
- Murphy, K.J., et al. "Chronic exposure of rats to cognition enhancing drugs produces a neuroplastic response identical to that obtained by complex environment rearing." Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 31, no. 1, 2006, pp. 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300810.
- Robinson, R.G., Jorge, R.E., Clarence-Smith, K. "Double-blind randomized treatment of poststroke depression using nefiracetam." J. Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci, vol. 20, no. 2, 2008, pp. 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.neuropsych.20.2.178.
- Hiramatsu, M., et al. "Effects of nefiracetam on amnesia animal models with neuronal dysfunctions." Behav Brain Res., vol. 83, no. 1–2, 1997, pp. 107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-4328(97)86053-6.
- Gouliaev, A.H., Senning, A. "Piracetam and other structurally related nootropics." Brain Res Brain Res Rev., vol. 19, no. 2, 1994, pp. 180–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(94)90011-6.
Information is for research and education only. Not for self-experimentation. Last updated: 4/12/2025.