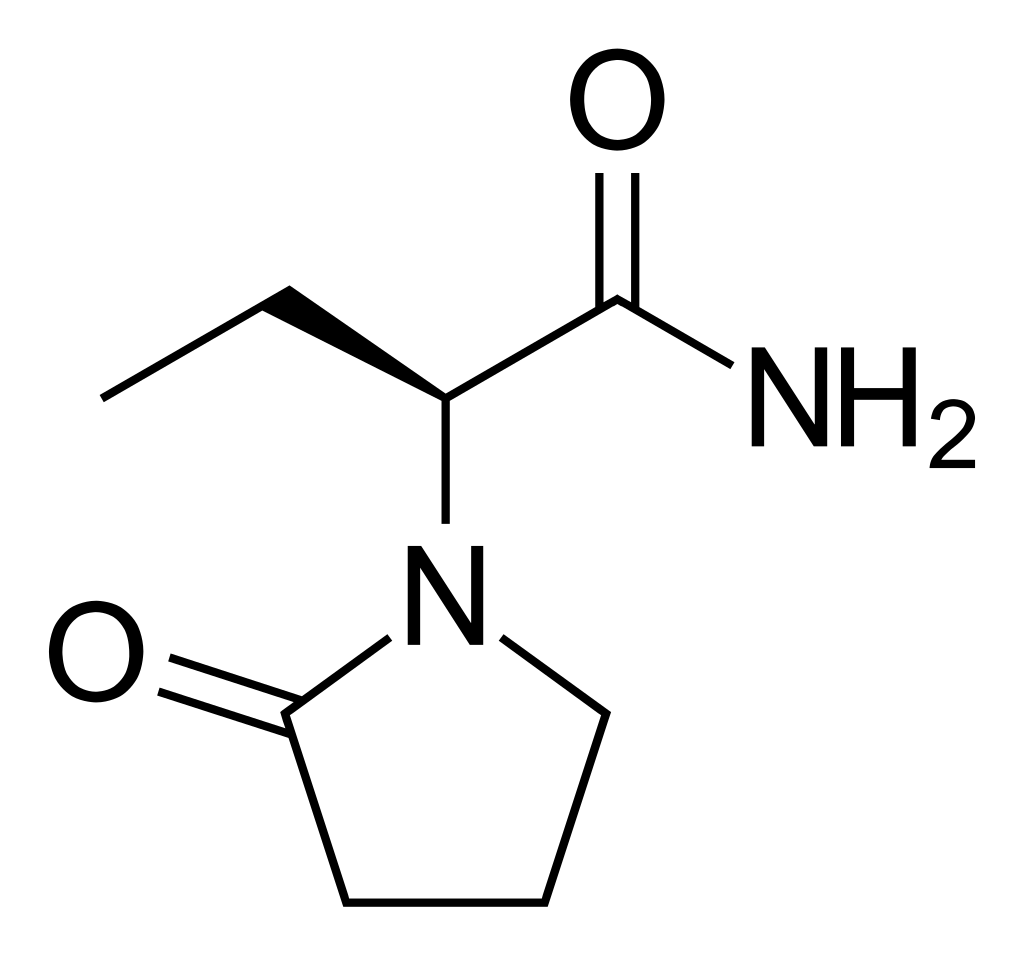
Levetiracetam
Keppra, Elepsia, Spritam (CAS 102767-28-2)
Levetiracetam is a clinically essential anticonvulsant racetam, used worldwide as Keppra and generics, indicated for various seizure types. Its action as an SV2A ligand is pharmacologically distinct among antiepileptics.
Also known as:
Formula
C₈H₁₄N₂O₂
Category
Racetam / Anticonvulsant
Half-Life
6–8 hrs
Legal Status
Rx Only (US/EU/AU/CA/UK/...)
Chemical Profile
Mechanism of Action
Unlike earlier racetams, levetiracetam acts primarily as a selective SV2A ligand: a synaptic vesicle protein involved in neuronal exocytosis and neurotransmitter release. This modulation is associated with a reduction in seizure activity and distinguishes levetiracetam pharmacologically from classic GABAergics and sodium channel blockers.
Preclinical & Clinical Evidence
SV2A Binding and Animal Research
Levetiracetam shows saturable, high affinity, stereospecific SV2A binding in mouse and human brain—and robust protection in genetic/induced seizure models.
Monotherapy and Add-on in Focal, Myoclonic, and Generalized Epilepsy
Extensive high-quality clinical evidence supports levetiracetam for monotherapy and adjunct use in partial, myoclonic, and tonic-clonic seizures in both adults and children; effectiveness and tolerability are generally high.
Other Confirmed Uses and Systematic Reviews
Effective as adjunct in myoclonic/tonic-clonic/generalized epilepsies, and in some cases of status epilepticus, with comparable or improved safety over alternatives.
Safety & Side Effects
Common reactions include fatigue, somnolence, dizziness, headache, and (esp. in children/adolescents) mood or behavioral symptoms. Severe/rare reactions: psychosis, suicidality, SJS/TEN, rash.
Regulatory & Legal Status
Global
- Rx only in all major jurisdictions (US, EU, CA, UK, AU, JP...)
- Listed as S4 in Australia, Rx only/controlled in many regions
- WHO Essential Medicines, >5 million US scripts/yr (2022)
Note: Levetiracetam is by prescription only; no OTC or supplement sale permitted.
History
Levetiracetam was discovered by UCB Pharma in the early 1990s via genetic seizure model screens, and later identified as the S-enantiomer of etiracetam. Approved US/Europe 1999–2000, now global first-line for epilepsy.

Premium Levetiracetam
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- First-in-class SV2A ligand anticonvulsant
- Wide spectrum: focal, myoclonic, generalized seizures
- Favorable safety/tolerability, generic availability
Considerations
- Prescription-only worldwide
- Behavioral/psychiatric adverse effects possible
- Not a cognitive enhancer: for epilepsy
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References
- Lynch, B.A., et al. "The synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is the binding site for the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, vol. 101, no. 26, 2004, pp. 9861–9866. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308208101.
- Lattanzi, S., et al. "Antiepileptic monotherapy in newly diagnosed focal epilepsy. A network meta-analysis." Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, vol. 139, no. 1, 2019, pp. 33–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.13025.
- Nevitt, S.J., et al. "Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data." Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2022(4): CD011412. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub4.
- Mbizvo, G.K., et al. "Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: An updated Cochrane Review." Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2.
- "Levetiracetam". PubChem Compound Summary, National Center for Biotechnology Information, CID 5284583. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5284583.
Information is for medical, scientific, and educational reference only. Last updated: 4/12/2025.