Cebaracetam
CGS-25248 | ZY-15119 | 4-chlorophenylpiracetam piperazine analogue
Cebaracetam is a synthetic, experimental racetam nootropic originally developed by Novartis in the 1990s, closely related to phenylpiracetam and RGPU-95. Clinical development was discontinued after phase 2, with no published results.
Developmental Names:
Formula
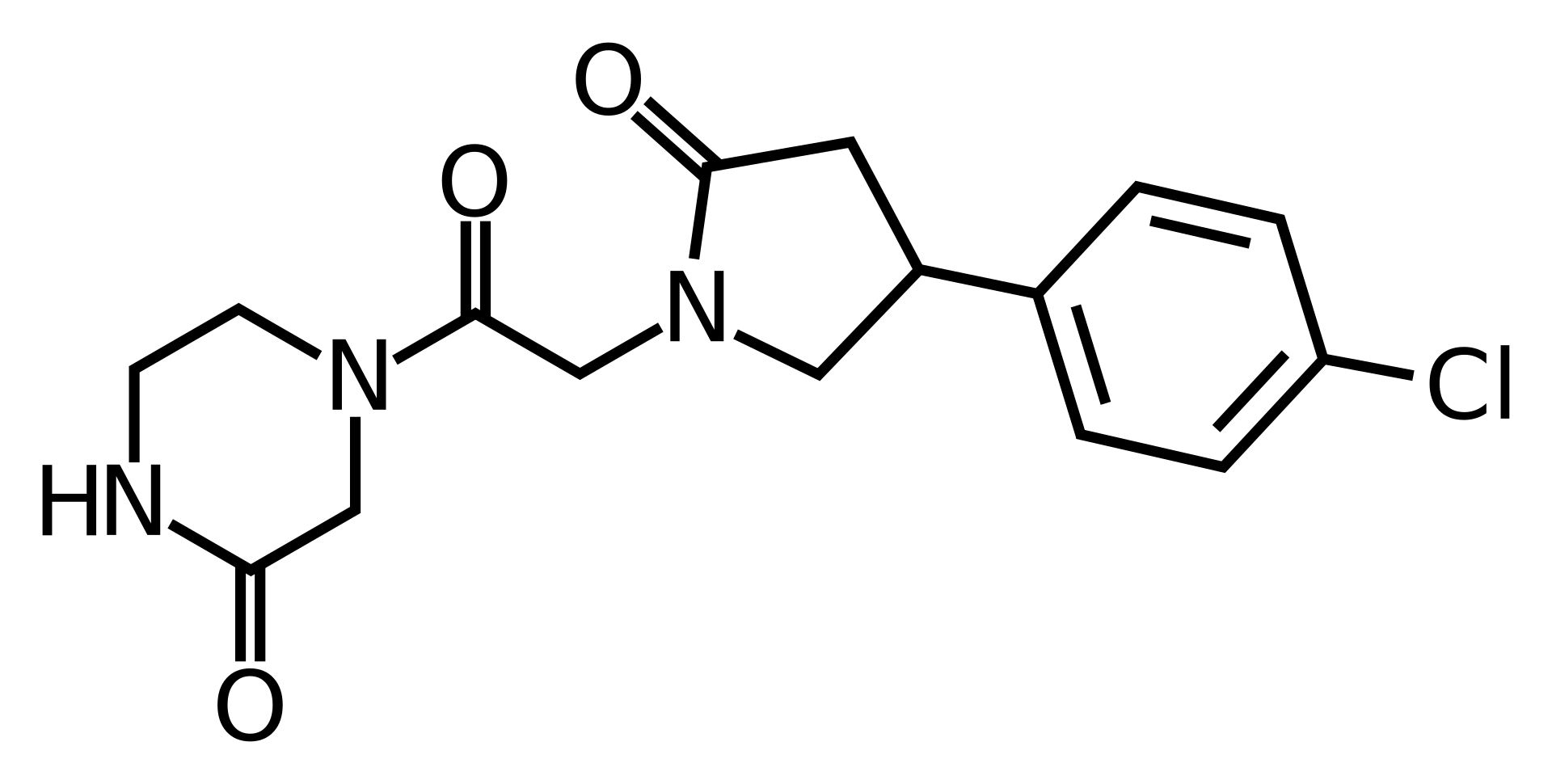
C₁₆H₁₈ClN₃O₃
Category
Racetam / Experimental
Half-Life
Unknown
Status
Not approved, research only
Chemical Profile
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of cebaracetam is unknown; it is presumed to act similarly to other racetams, but as of 2024, no definitive molecular targets have been confirmed in peer-reviewed literature. It is chemically a derivative of 4-chlorophenylpiracetam with a piperazin-2-one group.
Preclinical & Clinical Data
Treatment for Cognitive Disorders (Abandoned, Phase 2)
Cebaracetam reached phase 2 studies for cognition disorders, but all clinical data remain unpublished. Development was discontinued by Novartis in 1995.
AdisInsight Drug record
Analytical Pharmacokinetics in Human Urine (HPLC Method)
Analytical high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods to detect cebaracetam in biological fluids were validated, but pharmacokinetics and full animal/human disposition are unpublished.
D Chollet, P Künstner.
J Chromatogr. 1992 Jun;577(2):335–340.
PMID: 1400764
Relation to Phenylpiracetam and RGPU-95: Structure-Activity Studies
Cebaracetam is a 4-chlorophenylpiracetam piperazine analogue; SAR studies show the terminal amide replacement by piperazin-2-one. No published reports of cognitive enhancement or psychoactivity in animals/humans.
PubChem Compound ID 65919
Side Effects & Considerations
There are no published preclinical or clinical studies on cebaracetam’s side effect profile. Toxicology and acute safety profile are not established.
Regulatory & Legal Status
United States
- Not FDA approved for any medical use
- Unscheduled (not controlled or regulated), research chemical only
- May fall under analog act in some regions
- Not legally sold as a supplement/medicine
International
- No official regulatory status (not approved in EU, CA, AU, UK, etc)
- Not available as a pharmaceutical or supplement
- Research use only
Legal status advisory: Cebaracetam is not approved in any country; research use only where permitted. Not intended for human consumption.
Historical Context & Development
Cebaracetam (CGS-25248, ZY-15119) was developed in the early 1990s by Novartis as an experimental nootropic intended for the treatment of cognitive disorders. It reached phase 2 trials before development was abandoned, and has never been marketed. Cebaracetam is structurally a piperazine-modified, 4-chlorophenyl-substituted analogue of phenylpiracetam and RGPU-95.
No clinical efficacy data, indication, or adverse reactions have ever been published in full. The compound remains a curiosity for racetam chemists and nootropic drug historians.

Premium Cebaracetam
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- Structurally unique racetam; piperazine-modified phenylpiracetam analogue
- Valuable for structure–activity and SAR research
- Phase 2 trialled as a cognitive enhancer (unpublished results)
Considerations
- No approved medical use, no published safety data
- Not approved or marketed; research only
- Unknown human pharmacology or toxicity
- Legal status unclear in some jurisdictions
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References
Compiled from peer-reviewed literature, open-access chemical databases, and discontinued compound documentation. Last updated: 4/12/2025.
- "Cebaracetam". AdisInsight. 23 May 1995. AdisInsight Drug Record
- D Chollet, P Künstner. Fast systematic approach for the determination of drugs in biological fluids by fully automated high-performance liquid chromatography with on-line solid-phase extraction and automated cartridge exchange. Application to cebaracetam in human urine. Journal of Chromatography. 1992;577(2):335–340. PMID: 1400764
- "Cebaracetam". PubChem CID 65919, NIH Database. PubChem
- WHO. International Nonproprietary Names (INN) StemBook, 2018. link