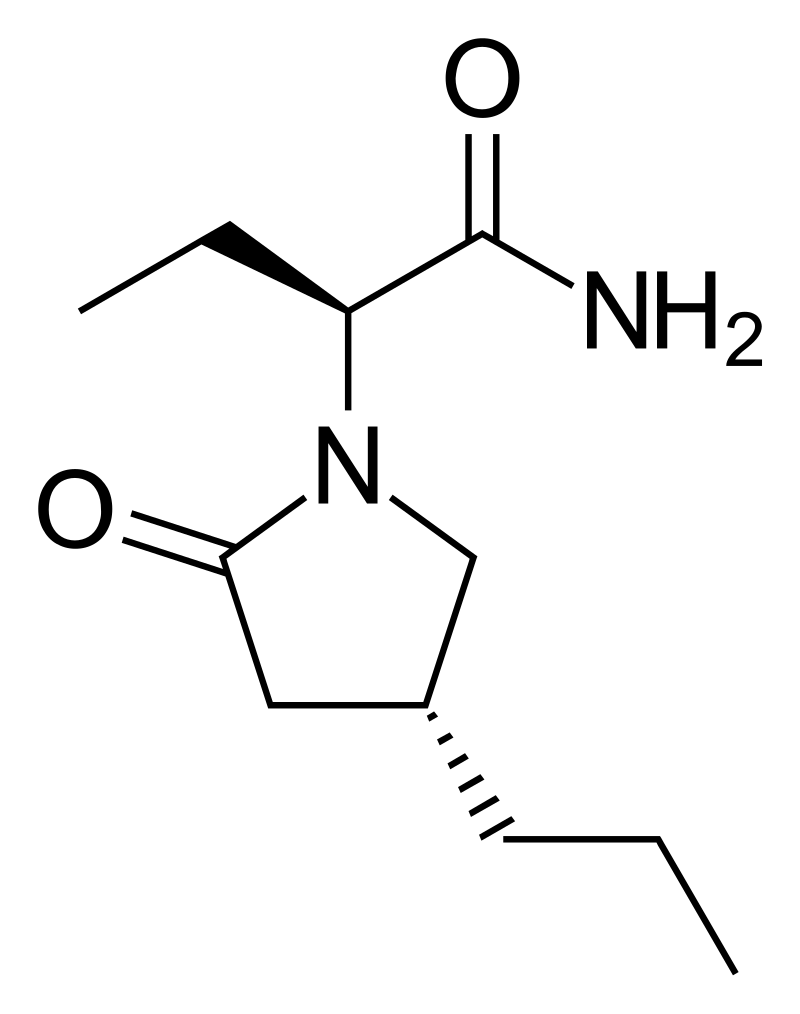
Brivaracetam
(2S)-2-[(4R)-2-oxo-4-propylpyrrolidin-1-yl]butanamide
A next-generation racetam anticonvulsant, Brivaracetam is a high-affinity ligand for SV2A, indicated as adjunct for partial-onset epileptic seizures where it matches or surpasses levetiracetam for efficacy and CNS tolerability.
Available as:
Formula
C₁₁H₂₀N₂O₂
Category
Racetam / Anticonvulsant
Half-Life
~8–9 hours
Standard Dose
50–200 mg/d
Chemical Profile
Mechanism of Action
Selective SV2A Ligand
Brivaracetam binds with high affinity (20x greater than levetiracetam) to the synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A), regulating vesicle exocytosis and neurotransmitter release. This action suppresses neuronal hyperexcitability and seizure spread.
[von Rosenstiel 2007, Matagne 2008, Rogawski 2016]
Glutamate Release Modulation
Brivaracetam reduces excitatory neurotransmitter (primarily glutamate) release during high-frequency firing, thus limiting the sustained excitatory transmission underlying many epilepsies.
Rapid CNS Penetration
Its high lipophilicity and minimal protein binding (<20%) allow for rapid brain entry and swift onset of action, outperforming levetiracetam in speed of CNS penetration.
Minimal off-target effects
Unlike many antiepileptics, Brivaracetam is highly selective for SV2A, with limited direct effects on sodium, potassium, or calcium channels, reducing its side-effect burden compared to older medications.
Clinical Applications & Efficacy
Adjunct for Partial-Onset Seizures
Used worldwide as add-on treatment for focal (partial) epilepsy, Brivaracetam shows robust efficacy in reducing seizure frequency with a favorable tolerability profile.
Efficacy and Tolerability in Intellectual Disability
Brivaracetam is as effective and tolerable for epilepsy in adults with intellectual disability as in the general population, offering a treatment for a group where options are often limited.
Rapid CNS Penetration—Useful for Acute Rescue
Brivaracetam's rapid brain entry allows for fast clinical effect; this property is especially notable in perioperative or emergency rescue settings.
Direct Conversion From Levetiracetam
Brivaracetam can be safely substituted for levetiracetam by established formula (50 mg brivaracetam for 1000 mg levetiracetam). Real-world studies suggest improved behavioral tolerability for some patients.
Pharmacokinetics Note
Brivaracetam is rapidly and fully absorbed after oral or IV dosing, with low protein binding (~20%), and eliminated mainly by hepatic hydrolysis & urinary metabolites. CYP2C19 poor metabolizers may need dose reduction.
Side Effects & Precautions
Common
- Sleepiness, somnolence
- Dizziness
- Nausea/vomiting
- Fatigue
- Headache
Neurobehavioral
- Irritability, aggression (rare)
- Depression, mood disturbance
- Psychotic symptoms (very rare)
- Risk may increase with rapid up-titration or history of psychiatric issues
Drug Interactions
- May increase phenytoin or carbamazepine-epoxide levels
- No significant interactions with most AEDs
- Avoid alcohol (increases impairment/sedation risks)
Tolerability Profile: Generally better than levetiracetam for behavioral AEs; lower risk of severe psychiatric events but monitor in susceptible patients.
Regulatory & Legal Status
United States & Canada
- FDA Approved (2016), Rx-only
- DEA Schedule V (lowest abuse potential)
- Health Canada approved (as Brivlera) 2016
- Generic approved by FDA (2022), not yet marketed as of 2024
World/Europe/Australia
- EU EMA Approved, Rx-only (2016)
- Australia: Schedule 4 (prescription only)
- Brazil: Class C1 controlled
- No meaningful recreational use or off-label abuse reported
Not a performance enhancer: Brivaracetam is not prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency as it lacks stimulating or athletic performance effects.
Historical Context
Developed by UCB as UCB-34714, brivaracetam was designed for enhanced SV2A affinity after the success of levetiracetam.
It demonstrated 10-fold greater preclinical potency, with clinical development starting in the early 2000s. Brivaracetam was granted EU approval in Jan 2016 and FDA approval Feb 2016 (as Briviact).
It is now a mainstay adjunctive drug for partial epilepsy, especially where rapid CNS action or improved tolerability over levetiracetam is desired.

Premium Brivaracetam
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- High-affinity SV2A modulation (20x stronger than levetiracetam)
- Rapid brain penetration for fast onset of action
- Better behavioral tolerability profile than levetiracetam
- Available in both oral and IV formulations
Considerations
- Prescription medication in most countries
- May cause drowsiness and affect coordination
- Potential interactions with other anticonvulsants
- CYP2C19 poor metabolizers may need dose adjustment
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References
This information is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare professional for patient-specific recommendations. See the official product literature for regulated indications and dosing.
- Bresnahan R, Panebianco M, Marson AG. Brivaracetam add‐on therapy for drug‐resistant epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022; 2022(3):CD011501. doi
- Allard J, Henley W, Sellers A, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of Brivaracetam in people with intellectual disability compared to those without intellectual disability. Epilepsy & Behavior. 2024 Sep;158:109906. doi
- Klein P, Diaz A, Gasalla T, Whitesides J. A review of the pharmacology and clinical efficacy of brivaracetam. Clinical Pharmacology: Advances and Applications. 2018;10:1-22. doi
- Asadi-Pooya AA, Patel AA, Trinka E, Mazurkiewicz-Beldzinska M, Cross JH, Welty TE. Recommendations for treatment strategies in people with epilepsy during times of shortage of antiseizure medications. Epileptic Disorders. 2022 Oct;24(5):751-764. doi
- Dean L. Brivaracetam Therapy and CYP2C19 Genotype. In: Medical Genetics Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2018. PubMed
- Sargentini-Maier ML, Espié P, Coquette A, Stockis A. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of 14C-brivaracetam, a novel SV2A ligand, in healthy subjects. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Jan;36(1):36-45. doi
Content based on peer-reviewed research, clinical studies, and pharmacological databases. Last updated: 4/12/2025