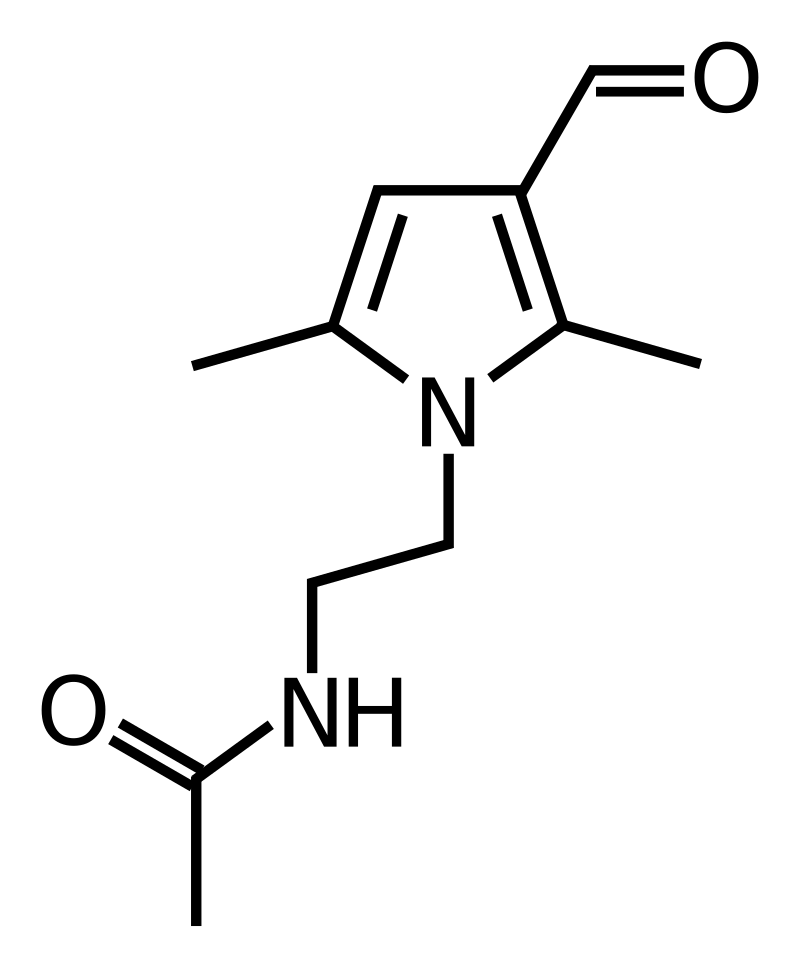
Aloracetam
C₁₁H₁₆N₂O₂
A lesser-studied member of the racetam family with potential cognitive enhancement properties. Current research on this compound is limited compared to other more established racetams.
Identification:
Formula
C₁₁H₁₆N₂O₂
Category
Racetam
Molar Mass
208.261 g/mol
Status
Investigational
Chemical Profile
Research Status: Aloracetam is primarily considered an investigational compound with limited published research compared to more established racetams. Information regarding its specific pharmacology and efficacy is currently sparse in the scientific literature.
Potential Mechanisms of Action
While specific research on aloracetam's mechanisms of action is limited, its membership in the racetam family suggests several potential neurobiological pathways:
Cholinergic System Modulation
Like many racetams, aloracetam may influence acetylcholine synthesis, release, or receptor binding. This neurotransmitter system is critical for learning, memory formation, and general cognitive function.
Glutamatergic Neurotransmission
Potential interaction with glutamate receptors, particularly AMPA receptors, which could enhance signal transmission and facilitate long-term potentiation (LTP), a key mechanism in memory formation.
Membrane Fluidity
May affect neuronal membrane properties, altering fluidity and influencing receptor function and signal transduction, which is a mechanism observed in other racetam compounds.
Neuroprotective Effects
Possible neuroprotective properties against various forms of neuronal damage, potentially through antioxidant mechanisms or optimization of cellular energy metabolism.
Research Limitation: It should be noted that the above mechanisms are hypothetical based on structural similarities with other racetams. Direct pharmacological studies specifically on aloracetam are currently limited in the published scientific literature.
Current Research Status
Aloracetam represents one of the less-studied compounds in the racetam family, with limited published clinical research. The current state of knowledge primarily consists of:
Preclinical Investigations
Most research on aloracetam has been conducted at the preclinical level, including in vitro studies and limited animal models. These studies have generally focused on characterizing the compound's basic pharmacological properties rather than specific therapeutic applications.
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies
Chemical structure analyses comparing aloracetam to other racetams have been conducted to better understand the relationship between molecular structure and cognitive enhancement properties within this class of compounds.
Clinical Research Gap
Unlike more established racetams such as piracetam, oxiracetam, and aniracetam, aloracetam has not been the subject of extensive clinical trials in humans. There are currently no published randomized controlled trials evaluating its efficacy for cognitive enhancement or treatment of neurological conditions.
Research Status Note: The current research landscape for aloracetam is characterized by significant knowledge gaps. While its chemical structure suggests potential nootropic effects similar to other racetams, these effects have not been thoroughly validated through rigorous scientific investigation. Researchers and potential users should be aware that most information about aloracetam's effects is extrapolated from structurally similar compounds rather than direct studies.
Hypothesized Applications
Based on structural similarities with better-studied racetams, researchers have hypothesized several potential applications for aloracetam, though these remain speculative until confirmed by rigorous clinical studies:
Cognitive Enhancement
Like other racetams, aloracetam might potentially enhance various aspects of cognition, including memory formation, learning capacity, attention, and information processing. However, the magnitude and specific profile of these effects remain undetermined.
Neuroprotection
Theoretical neuroprotective properties might make it relevant to conditions involving neuronal damage or degeneration, though no clinical evidence currently supports this application.
Research Tool
Aloracetam may serve as a valuable compound for structure-activity relationship studies within the racetam family, helping researchers better understand the relationship between chemical structure and cognitive effects in this class of nootropics.
Potential Unique Properties
The unique structural elements of aloracetam might confer properties distinct from other racetams, potentially offering a different profile of effects that could be valuable in specific cognitive or neurological conditions.
Important Consideration: The applications listed above are largely theoretical and based on extrapolation from other racetams rather than direct evidence for aloracetam specifically. Further research, including well-designed preclinical studies and clinical trials, would be necessary to establish the actual efficacy and safety profile of aloracetam for any of these potential applications.
Regulatory Status
United States
- •Not FDA approved for medical use
- •Unscheduled by the DEA
- •Exists primarily as a research compound
- •Not approved for use in dietary supplements
International Status
- •No known countries have approved it for prescription use
- •Primarily exists as a research compound globally
- •Regulatory status varies by country
- •Not included in major pharmacopeia
Regulatory Note: Unlike several other racetams which have received approval as prescription medications in various countries, aloracetam has not undergone the clinical trials necessary for medical approval. Its regulatory status reflects its limited research profile rather than any specific safety concerns.
Future Research Directions
To establish aloracetam as a viable nootropic or therapeutic agent, several key research areas need to be addressed:
- Comprehensive Pharmacological Profiling: Detailed studies of pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and metabolic pathways.
- Mechanism of Action Studies: Investigation of specific receptor interactions, neurotransmitter effects, and cellular signaling pathways influenced by aloracetam.
- Preclinical Efficacy Models: Behavioral and cognitive testing in animal models to establish baseline efficacy for various potential applications.
- Safety and Toxicity Evaluations: Comprehensive assessment of short and long-term safety profile, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
- Clinical Trials: Eventually, properly designed human studies would be needed to establish efficacy, safety, and optimal dosing regimens.
The current research landscape for aloracetam reflects the broader challenges in nootropic research, including limited funding for compounds without patent protection, methodological challenges in measuring cognitive effects, and regulatory hurdles. Future research would benefit from standardized approaches to cognitive assessment and greater collaboration between academic and industry researchers.

Premium Aloracetam
Enhance your cognitive performance with science-backed, high-quality nootropics.
Benefits
- Novel racetam structure with unique potential
- Theoretical cognitive enhancement properties
- Subject of ongoing neurochemical research
- Contributes to racetam structure-activity relationship knowledge
Considerations
- Limited published clinical research available
- No established dosage guidelines
- Not approved for medical use in any country
- Limited long-term safety data
Free shipping on orders above $50
Scientific References & Resources
This information is provided for educational purposes only. Given the limited research on aloracetam, much of the information presented is based on extrapolation from structurally similar compounds and general principles of racetam pharmacology.
- PubChem CID: 178134. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- ChemSpider ID: 155069. Royal Society of Chemistry.
- Malykh AG, Sadaie MR (2010). Piracetam and piracetam-like drugs: from basic science to novel clinical applications to CNS disorders. Drugs, 70(3):287-312.
- Gualtieri F, et al. (2002). Design and study of piracetam-like nootropics, controversial members of the problematic class of cognition-enhancing drugs. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 8(2):125-138.
Content based on chemical databases and principles of racetam pharmacology. Last updated: 4/12/2025